Projects
Transformers are one of the primary components for the transmission and distribution of electrical energy. Their design results mainly from the range of application, the construction, the rated power and the voltage level. There are also various special purpose transformers such as furnace transformers, which are basically in the range of power transformers as far as rated power and rated voltage are concerned. Furnace transformers are characterized by very high secondary currents and wide secondary voltage regulation in order to cope with the furnace needs, depending on the particular kind of cycle requested.
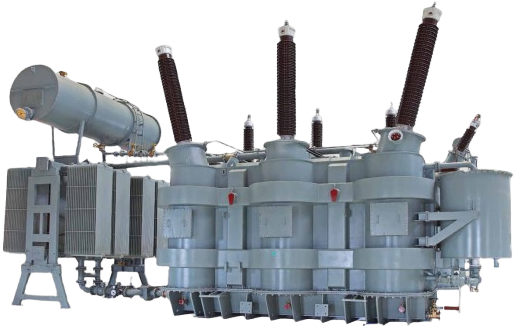
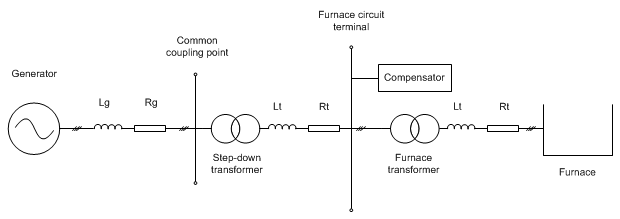
For many years, Electrical Arc Furnace (EAF) power transformers have been meeting very high supply needs of the steel industry's arc furnaces around the world. EAF transformers are suitable for steel furnaces, ladle furnaces (LF) and ferroalloy furnaces. They work under critical and severe conditions caused by overcurrents and overvoltages generated by short circuits in the furnaces. Arc furnace transformers are used for melting scrap metal. Usually when there is an EAF there is also an LF that is used to refine the metal melted by the arc furnace. Such kind of transformers are three phases.
We have experience in supplying the following types of transformers
| Transformer Type | Capacity (MVA) |
|---|---|
| Three Phase (EAF) Transformer | 90 MVA |
| Three Phase (LF) Transformer | 18 MVA |
| Three Phase (LF) Transformer | 13 MVA |
| Three Phase (POWER) Transformer | 63 MVA |
| Three Phase (EAF) Transformer | 45 MVA |
| Three Phase (EAF) Transformer | 85 MVA |
| Three Phase (EAF) Transformer | 130 MVA |
| Three Phase (POWER) Transformer | 160 MVA |
| Three Phase (LF) Transformer | 24 MVA |
Supply of Special Reducer, Mechanical Holding Devices and other equipment related to converter steel making for Bokaro Steel Plant (SAIL) in India. Generally, the group is currently involved in the execution of converter revamp project at SAIL. This project is one of a kind in terms of the complexity and logistics involved. Among other spare parts for converter, the equipment shipped includes Mesh Holding Device, Driving Sprockets and Chains, Special Reducer, Gear Box etc.



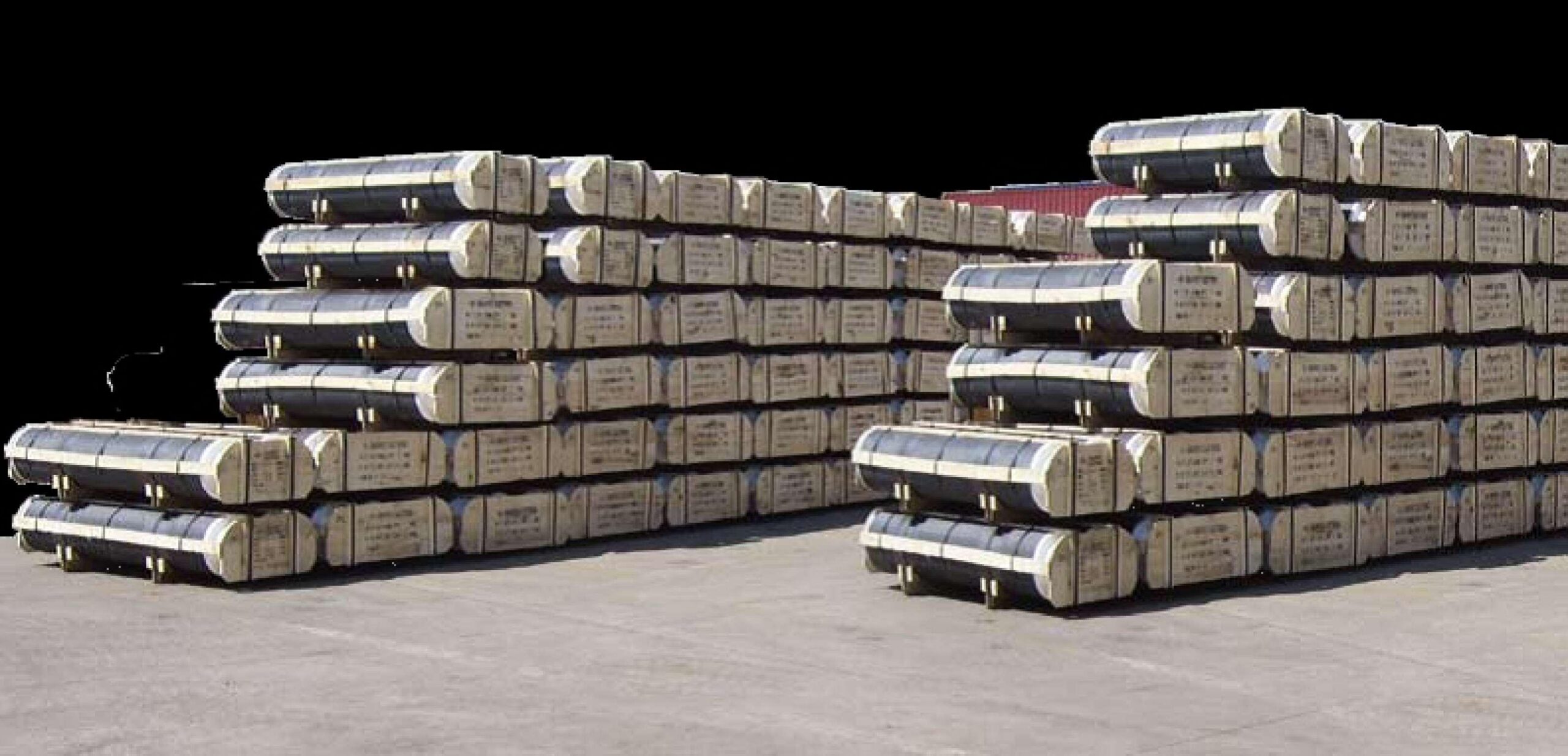
Graphite Electrodes
Leveraging our global network, reach, we offer turnkey solutions in complex projects in the field of ferrous metallurgy. We partner with Azovmash, one of the world's leading manufacturer of iron making, steel making equipment and carriage/lifting equipment. We have delivered complex projects across various geographies, like supply and commissioning of Graphite Electrodes f rom major Chinese manufacturers to Azovmash and Dneprospetsstal in Ukraine. Graphite electrodes are widely used in steel, smelting non-ferrous smelting and silicon, phosphorus, etc. We can offer various grades and specifications of the graphite electrode with low resistance, high density, strong antioxidant properties, high processing precision, etc, satisfying the needs of different users. The offered products all meet international quality standards.
Physico-Chemical Specifications of HP Graphite Electrode :
| Item | Unit | Ø200 ~ Ø400 | Ø450 ~ Ø500 | Ø550 ~ Ø600 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal | Typical | Nominal | Typical | Nominal | Typical | ||
| Specific Resistance – Electrode | μΩ·m | 6.5 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 6.0 |
| Specific Resistance – Nipple | μΩ·m | 5.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 | 4.5 |
| Bending Strength – Electrode | MPa | 10.5 | - | 10.0 | - | 10.0 | - |
| Bending Strength – Nipple | MPa | 19.0 | - | 19.0 | - | 19.0 | - |
| Young’s Modulus – Electrode | GPa | 12.0 | - | 12.0 | - | 12.0 | - |
| Young’s Modulus – Nipple | GPa | 16.0 | - | 16.0 | - | 16.0 | - |
| Bulk Density – Electrode | g/cm³ | 1.65 | 1.68 | 1.65 | 1.68 | 1.66 | 1.68 |
| Bulk Density – Nipple | g/cm³ | 1.75 | 1.78 | 1.75 | 1.78 | 1.75 | 1.78 |
| CTE (100–600 °C) – Electrode | ×10⁻⁶/°C | 2.40 | - | 2.40 | - | 2.40 | - |
| CTE (100–600 °C) – Nipple | ×10⁻⁶/°C | 2.20 | - | 2.20 | - | 2.20 | - |
| Ash Content (for reference only) | % | 0.30 | - | 0.30 | - | 0.30 | - |
Physico-Chemical Specifications of UHP Graphite Electrode :
| Item | Unit | Ø200 ~ Ø400 | Ø450 ~ Ø500 | Ø550 ~ Ø600 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal | Typical | Nominal | Typical | Nominal | Typical | ||
| Specific Resistance – Electrode | μΩ·m | 5.5 | 5.0 | 5.5 | 5.0 | 5.5 | 4.8 |
| Specific Resistance – Nipple | μΩ·m | 4.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 |
| Bending Strength – Electrode | MPa | 11.0 | - | 11.0 | - | 12.0 | - |
| Bending Strength – Nipple | MPa | 20.0 | - | 20.0 | - | 20.0 | - |
| Young’s Modulus – Electrode | GPa | 14.0 | - | 14.0 | - | 14.0 | - |
| Young’s Modulus – Nipple | GPa | 18.0 | - | 18.0 | - | 18.0 | - |
| Bulk Density – Electrode | g/cm³ | 1.68 | 1.72 | 1.68 | 1.72 | 1.68 | 1.72 |
| Bulk Density – Nipple | g/cm³ | 1.78 | 1.80 | 1.78 | 1.80 | 1.80 | 1.82 |
| CTE (100–600 °C) – Electrode | ×10⁻⁶/°C | 1.50 | - | 1.50 | - | 1.40 | - |
| CTE (100–600 °C) – Nipple | ×10⁻⁶/°C | 1.40 | - | 1.40 | - | 1.20 | - |
| Ash Content (for reference only) | % | 0.30 | - | 0.30 | - | 0.30 | - |
Specification and Allowance of Graphite Electrode :
| Nominal Diameter (mm) | Nominal Diameter (Inch) | Actual Diameter Max (mm) | Actual Diameter Min (mm) | Nominal Length (mm) | Nominal Length (Inch) | Length Allowance (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 8 | 205 | 201 | 1600 / 1800 | 60 | ± 100 |
| 250 | 10 | 256 | 252 | 1600 / 1800 | 60 / 72 | ± 100 |
| 300 | 12 | 307 | 303 | 1800 | 72 | ± 100 |
| 350 | 14 | 357 | 353 | 1800 | 72 | ± 100 |
| 400 | 16 | 409 | 404 | 1800 / 2100 | 72 / 84 | ± 100 |
| 450 | 18 | 460 | 455 | 1800 / 2100 | 72 / 84 | ± 100 |
| 500 | 20 | 511 | 506 | 1800 / 2100 | 72 / 84 | ± 100 |
| 550 | 22 | 562 | 556 | 2100 / 2400 | 84 / 96 | ± 100 |
| 600 | 24 | 613 | 607 | 2100 / 2400 | 84 / 96 | ± 100 |

