
Introduction
Steelmont is committed to innovation, efficiency, and environmental sustainability in beneficiation technology.
Steelmont specializes in designing, manufacturing and delivering state-of-the-art Carbon Enrichment Units with customized support for the needs of various industries as mentioned below ensuring superior quality and efficiency
- DRI/Sponge Iron Plants
- Cement Plants
- Ferro Alloy Plants
- Power Plants, etc.
Service engineers available for the maintenance and smooth operations of the beneficiation plant
Importance of Coal Beneficiation
Coal beneficiation is a critical process in the coal industry that enhances the quality of raw coal by removing impurities like ash, soil, rock, and other non-combustible materials. This ensures optimal performance in various industrial applications.
Benefits of Beneficiation Plant
- Improved Quality: Increases the calorific value and reduces ash content.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Enhances combustion efficiency in DRI plants, power plants, and other industrial processes. Extends kiln life by minimizing accretion formation, reduces heat loss, and improves overall productivity.
- Environmental Compliance: Lowers harmful emissions by reducing impurities.
- Cost Savings: Reduces transportation costs by eliminating unwanted material.
- Industry-Ready Coal: Produces cleaner, market-ready coal for various uses.
Environmental Compliance
Dust control:
Visible Dust Control:
Dust-generating activities stop when visible dust dispersion occurs or when wind speeds exceed:
- 8 m/s (Wind Force 4) for dust classes S1 and S2.
- 14 m/s (Wind Force 6) for dust class S3.
- 20 m/s (Wind Force 8) for dust classes S4 and S5.
- Handling, Storage, and Transportation
- Low-Dust Grippers: Only grippers with overlapping blades or equivalent systems are allowed for loading/unloading to minimize dust.
Drop Heights: The drop height for materials (e.g., from conveyors, grippers) do not exceed 1 meter to prevent dust dispersion.
Moisture Management: Storage piles are kept moist with water spray systems, crust-forming agents, or covered with tarps to reduce emissions. - Monitoring and Reporting:
- Annual dust emission reports include:
Total emissions broken down by three-month intervals.
Impacts on particulate matter (PM) background levels.
A documented dust measurement system monitor emissions from key activities such as storage, transshipment, and transportation. - Standards Followed:
Dutch Emission Guidelines (NeR), September 2000 edition:
Dust classes (S1 to S5) are based on NeR standards, which dictate handling and emission control measures.
Filters for dust extraction systems must meet Section 3.2.2 of the NeR, ensuring effective capture of particulate matter. - Best Available Techniques (BAT):
Measures comply with BAT principles and are aligned with the BREF “Final Draft Reference Document on Emissions from Storage.”
Water Recycling
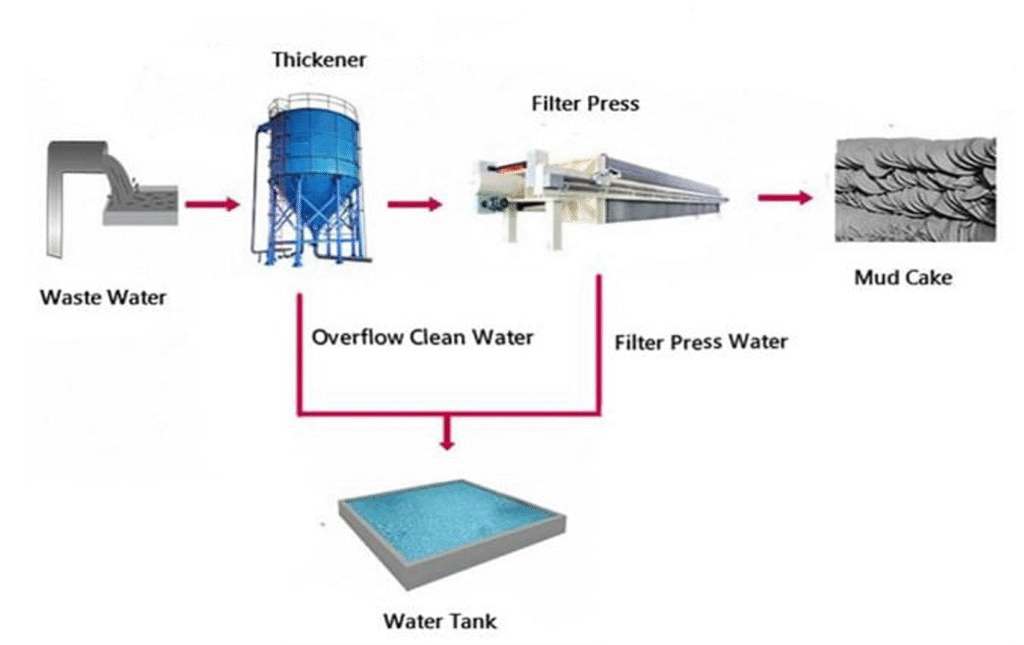
- Closed-Loop System: All water is treated and reused on-site to prevent wastewater discharge.
- Sludge Dewatering:Fine coal sludge is processed in a belt filter-press for reuse or shipment.
- Zero Wastewater Policy: Closed-Loop Water System: Prevents wastewater discharge by recycling and treating all water used.
Entire Beneficiation Plant Layout
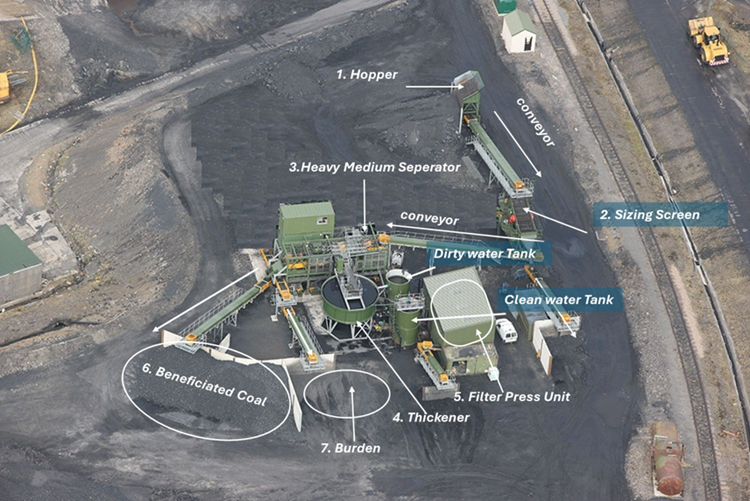
- Hopper & Conveyors:
Coal feeding conveyor to separator with coal loading hopper by loaders and feeder for uniform feeding.
Inclined conveyor that will take washing products from under the mobile separator to the stockpile - Sizing Screen Unit:
To separate materials by size. - Heavy Medium Seperator:
A modular unit designed for efficient coal beneficiation of +5 mm. - Thickener:
For dewatering and recovering process water. - Filter Press Unit:
To extract water from the slurry, producing filter cakes. - Beneficiated Coal:
Output storage area for cleaned coal. - Burden:
Storage area for waste material.
Our Approach
Our specialists follow and create tailored beneficiation processes based on the unique requirements of each client, ensuring efficiency, quality, and compliance with environmental norms

Sustainability and Benefits
– High Recovery Rates:
– Clean Coal Yield: 60-80%, providing high-quality fuel for energy production.
– Energy Coal Yield: 10-30%, ensuring no material is wasted during processing.
– By-Products:
– Clean Coal: High-grade fuel.
– Energy Coal: Secondary product with a calorific value of 4000 -6000 kcal/kg.
-Burden: Incorporated into finished products.
– Land Reclamation:
– Tailings are repurposed to reclaim degraded land.
– Backfilling in Mines:
– Tailings are used as backfill material to stabilize the ground.
– Building and Construction Materials:
– Tailings/cake are used to produce cement, bricks, and road base materials.
– Recovery of Valuable Minerals:
– Technologies recover trace valuable minerals from tailings.
– Energy Production:
– Coal fines and residuals are recovered for fuel or compacted into briquettes.
– Soil Amendments:
– Treated tailings are used in agriculture or landscaping.
– Water Management and Filtration:
– Tailings are used in sediment traps and for erosion prevention.
– Geopolymer Production:
– Rich tailings are used to produce eco-friendly alternatives to cement.
Conclusion:-
The coal enrichment plant is a highly efficient and environmentally compliant operation, combining state-of-the-art processing techniques with sustainable practices. Its closed-loop systems, minimal waste output, and adherence to environmental regulations ensure that the plant operates with minimal environmental impact while producing high-quality coal products for diverse applications.
